WordPress User Roles And Permissions
There are times when, as website owners, you’ll find the need to allow others onto your site. This could be for teams of collaborating writers, or SEO consultants who need to access your site to help.
However, allowing people onto your site has potential risks, you wouldn’t want someone deleting your posts or changing your site in a negative way. Giving full access to your website to someone who has limited knowledge on WordPress and your site’s settings can be dangerous. This is easily avoided, though, thanks to the handy feature found on all WordPress sites – User Roles.
In the following post, we’ll explore the different user roles WordPress offers, as well as the permissions given to each user. This is a simple look into WordPress roles explained and how you can use this feature to better your website.

WordPress Roles and Capabilities
There are 6 default user roles on WordPress. Here is a list of roles you can find for WordPress users:
- Subscriber
- Contributor
- Author
- Editor
- Administrator
- Super Administrator
The subscriber is the user who signs up to your site from the front end. They will only be able to read and view your site, and will often get email notifications when you post new content (if you have that option set up).
The Super Administrator is an option for a WordPress Multisite website. This user is given full permissions for all your sub-sites, whereas each sub-site would have its own admin.
What is a WordPress Contributor?
A contributor user on WordPress is able to add new drafts, edit their own drafts, and delete their drafts. They cannot publish posts – this must be done by an editor, and they can’t edit or delete any published posts.
In terms of security, when dealing with larger teams of writers, this user role is safe and easy to handle. Contributor users can see pending comments but have no access to approving or rejecting them. They are also unable to access site files, site settings, plugins, or any other part of the backend.

WordPress Author vs Contributor
Much like the Contributor, WP Author roles are solely to add content. The difference, however, is that Authors can publish their work. They are also able to delete their own published posts and drafts, as well as edit any of their own posts.
As an author, the user can add posts, edit their posts, and delete their own posts – drafts and published. They can’t edit or delete posts published by other users, and they can see comments but also can’t approve or reject them.
These users can add their posts to existing categories but cannot add or remove categories. They can, however, add new tags for their posts. Authors do not have permission to access any of the settings, they can’t see, add, or remove plugins, and they have no access to the site theme.
WordPress Author vs Editor
While the author is able to make changes to their own content, WordPress Editor roles are there for managing all content on your site.
Editors, as the name suggests, are there to edit and monitor ALL WordPress posts. They have the ability to add, edit, publish, and delete any and all posts. They can also moderate comments, add and remove categories, and access any other content-related backend sections.
Editors cannot, however, see or change the site’s plugins, settings, or users.

WordPress Editor vs Admin
While Editors have full control of your site’s content, the admin users have full control of everything else, as well as the content. If you’re running a standard WP website, the default user (you), will be the admin.
This WP role has permission to add & remove users, as well as change their roles and permissions. The admin can add and remove plugins, change site settings, and adjust the theme.
Admins have all the permissions that editors do, with the added access to the full backend of the site.

Selecting WordPress User Permissions
If you’re needing to add users to your site, the best way to go about it is to first figure out what you need the user to do on your site. If they are simply going to write posts for you, then contributor or author roles work perfectly.
To be able to make changes to already existing posts, perhaps to optimize your content, the user would need Editor role permissions. For anything else, such as adding or removing plugins, and even using some plugins (like the Redirection plugin), you’d have to add admin users.
It’s handy to remember that you can add users and change their permissions at any time. Only admins can do this, though, so if you do make anyone else admin on your site, make sure that you can trust them.
How to Add Users & Change Permissions
To add a user to your site, simply follow these steps:
#1 Login to the backend Dashboard of your WP website.
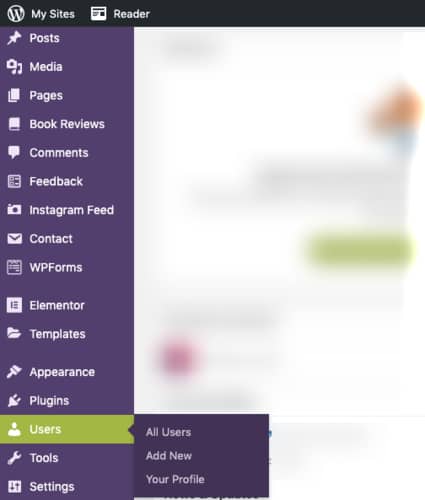
#2 Scroll down the toolbar on the left side of your screen and click on ‘Users’. Then click on ‘Add New’.
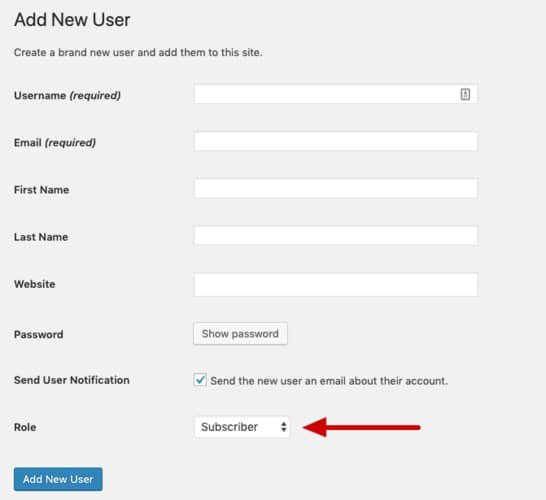
#3 Fill in the user’s details as requested in the form. Select the user role, and click on the ‘Add New User’ button.
The user will then get an email invitation and a link to activate their login details to your site.
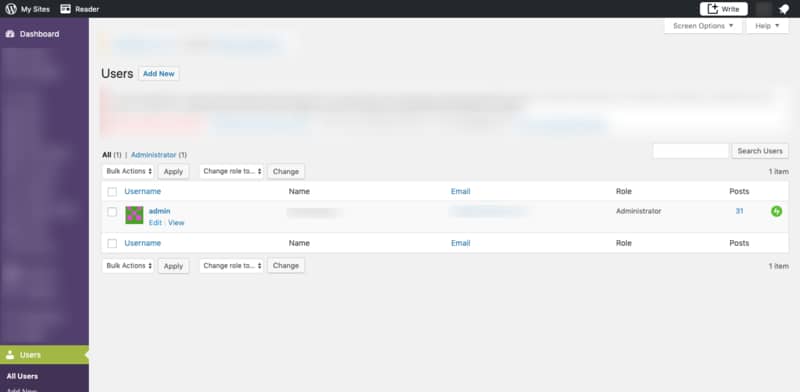
To change an existing user’s permissions, instead of clicking on ‘Add New’, select the ‘All Users’ option. You’ll then be able to see a list of your WordPress users.
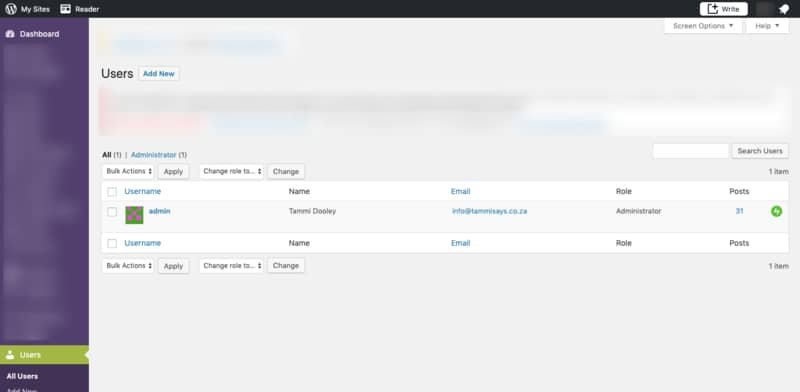
Hover just below the user name, and click ‘Edit’. From there, you can edit the user and change their role.
Final Thoughts
As with any sharing and collaborating online, adding WP roles to your site should be done wisely. Be sure that the users you create are trustworthy, and have the correct level of permissions for the job that they need to do.
Once you understand the WordPress permission levels, adding users, and giving them roles and permissions becomes quite easy. It’s an extremely handy feature to use when working with a team.